Render bagplots from tagged data comprising medians, hulls, contours, and outlier specifications.
Usage
geom_bagplot(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "bagplot",
position = "identity",
...,
bag.linewidth = sync(),
bag.linetype = sync(),
bag.colour = "black",
bag.color = NULL,
bag.fill = sync(),
bag.alpha = NA,
median.shape = 21L,
median.stroke = sync(),
median.size = 5,
median.colour = sync(),
median.color = NULL,
median.fill = "white",
median.alpha = NA,
fence.linewidth = 0.25,
fence.linetype = 0L,
fence.colour = sync(),
fence.color = NULL,
fence.fill = sync(),
fence.alpha = 0.25,
outlier.shape = sync(),
outlier.stroke = sync(),
outlier.size = sync(),
outlier.colour = sync(),
outlier.color = NULL,
outlier.fill = NA,
outlier.alpha = NA,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). If specified andinherit.aes = TRUE(the default), it is combined with the default mapping at the top level of the plot. You must supplymappingif there is no plot mapping.- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options:
If
NULL, the default, the data is inherited from the plot data as specified in the call toggplot().A
data.frame, or other object, will override the plot data. All objects will be fortified to produce a data frame. Seefortify()for which variables will be created.A
functionwill be called with a single argument, the plot data. The return value must be adata.frame, and will be used as the layer data. Afunctioncan be created from aformula(e.g.~ head(.x, 10)).- stat
The statistical transformation to use on the data for this layer. When using a
geom_*()function to construct a layer, thestatargument can be used the override the default coupling between geoms and stats. Thestatargument accepts the following:A
Statggproto subclass, for exampleStatCount.A string naming the stat. To give the stat as a string, strip the function name of the
stat_prefix. For example, to usestat_count(), give the stat as"count".For more information and other ways to specify the stat, see the layer stat documentation.
- position
A position adjustment to use on the data for this layer. This can be used in various ways, including to prevent overplotting and improving the display. The
positionargument accepts the following:The result of calling a position function, such as
position_jitter(). This method allows for passing extra arguments to the position.A string naming the position adjustment. To give the position as a string, strip the function name of the
position_prefix. For example, to useposition_jitter(), give the position as"jitter".For more information and other ways to specify the position, see the layer position documentation.
- ...
Additional arguments passed to
ggplot2::layer().- bag.linetype, bag.linewidth, bag.colour, bag.color, bag.fill, bag.alpha
Default aesthetics for bags. Set to
sync()to inherit from the data's aesthetics or toNULLto use the data's aesthetics.- median.shape, median.stroke, median.size, median.colour, median.color, median.fill, median.alpha
Default aesthetics for medians. Set to
sync()to inherit from the data's aesthetics or toNULLto use the data's aesthetics.- fence.linetype, fence.linewidth, fence.colour, fence.color, fence.fill, fence.alpha
Default aesthetics for fences. Set to
sync()to inherit from the data's aesthetics or toNULLto use the data's aesthetics.- outlier.shape, outlier.stroke, outlier.size, outlier.colour, outlier.color, outlier.fill, outlier.alpha
Default aesthetics for outliers. Set to
sync()to inherit from the data's aesthetics or toNULLto use the data's aesthetics.- na.rm
Passed to
ggplot2::layer().- show.legend
logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
NA, the default, includes if any aesthetics are mapped.FALSEnever includes, andTRUEalways includes. It can also be a named logical vector to finely select the aesthetics to display.- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.borders().
Value
A ggproto layer.
Details
geom_bagplot() is designed to pair with stat_bagplot(),
analogously to the pairing of ggplot2::geom_boxplot() with
ggplot2::stat_boxplot().
Because the optional components are more expensive to compute in this
setting, they are controlled by parameters passed to the stat. Auxiliary
aesthetics like median.colour are available that override auxiliary
defaults, and these in turn override the standard defaults. Auxiliary
defaults also take effect when auxiliary aesthetics are passed NULL, so
that stat_bagplot() and geom_bagplot() have the same default behavior.
Pass sync() (instead of NULL, as in ggplot2::geom_boxplot()) to
synchronize an auxiliary aesthetic with its standard counterpart.
WARNING: The trade-off between precision and runtime is greater for depth estimation than for density estimation. At the resolution of the default \(100 \times 100\) grid, basic examples may vary noticeably when starting from different random seeds.
Biplot layers
ggbiplot() uses ggplot2::fortify() internally to produce a single data
frame with a .matrix column distinguishing the subjects ("rows") and
variables ("cols"). The stat layers stat_rows() and stat_cols() simply
filter the data frame to one of these two.
The geom layers geom_rows_*() and geom_cols_*() call the corresponding
stat in order to render plot elements for the corresponding factor matrix.
geom_dims_*() selects a default matrix based on common practice, e.g.
points for rows and arrows for columns.
Aesthetics
geom_bagplot() understands the following aesthetics (required aesthetics
are in bold):
xycomponentlinewidthlinetypecolourfillalphashapestrokesizegroup
See also
Other geom layers:
geom_axis(),
geom_interpolation(),
geom_isoline(),
geom_lineranges(),
geom_origin(),
geom_rule(),
geom_text_radiate(),
geom_vector()
Examples
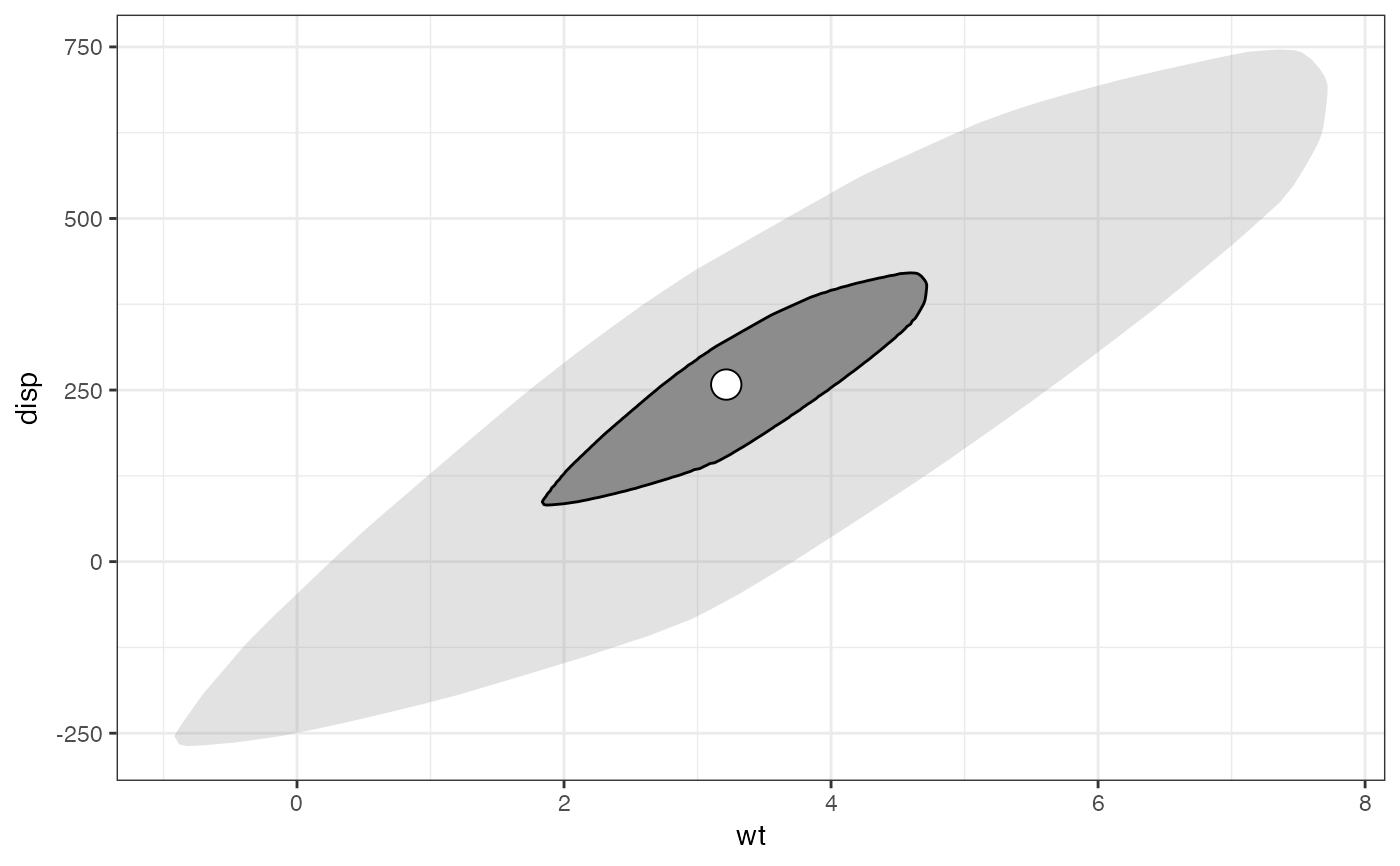
# Motor Trends base plot with factorized cylinder counts
p <- mtcars |>
transform(cyl = factor(cyl)) |>
ggplot(aes(x = wt, y = disp)) +
theme_bw()
# basic bagplot
p + geom_bagplot()
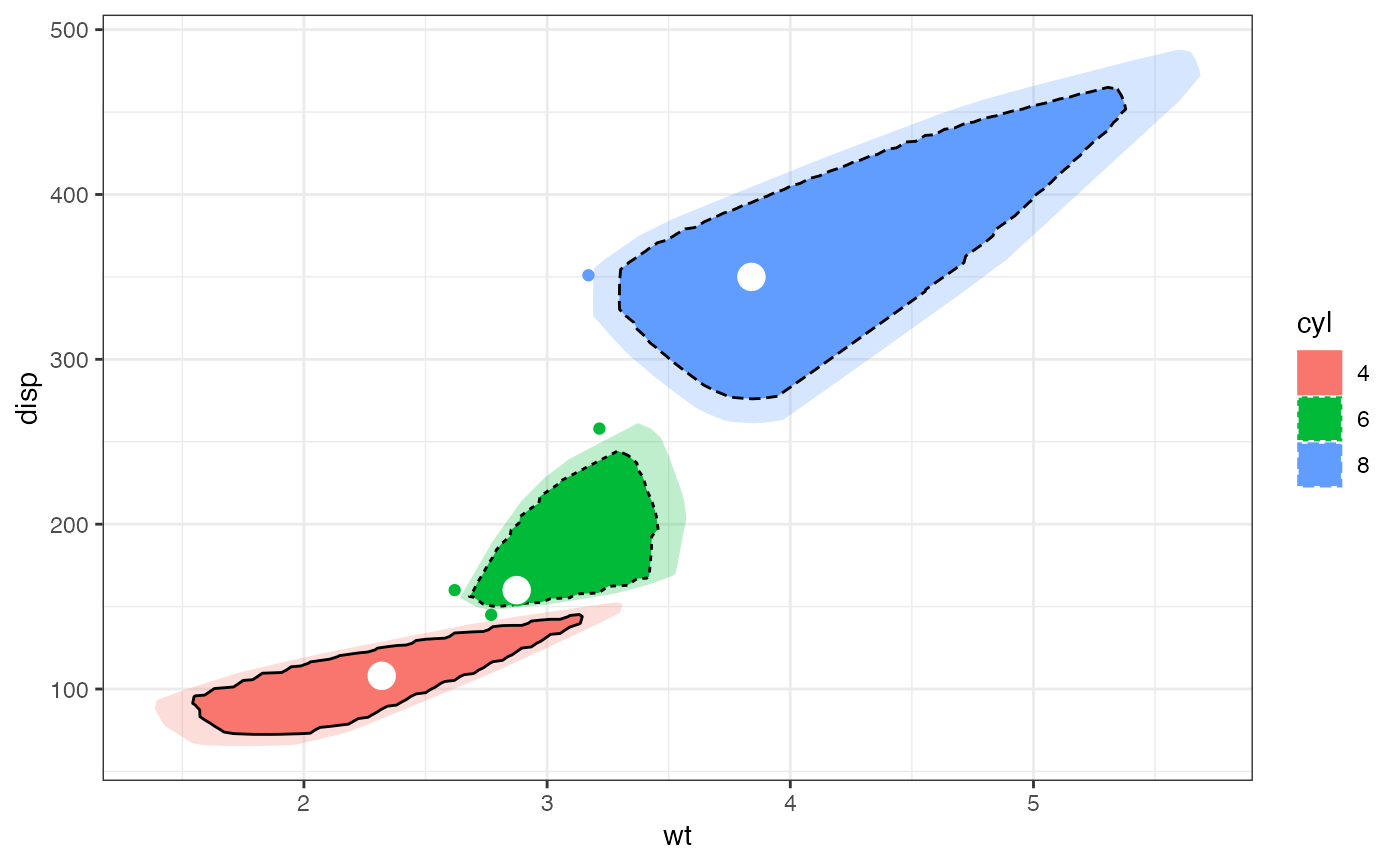
 # group by cylinder count
p + geom_bagplot(
fraction = 0.4, coef = 1.2,
aes(fill = cyl, linetype = cyl, color = cyl)
)
# group by cylinder count
p + geom_bagplot(
fraction = 0.4, coef = 1.2,
aes(fill = cyl, linetype = cyl, color = cyl)
)
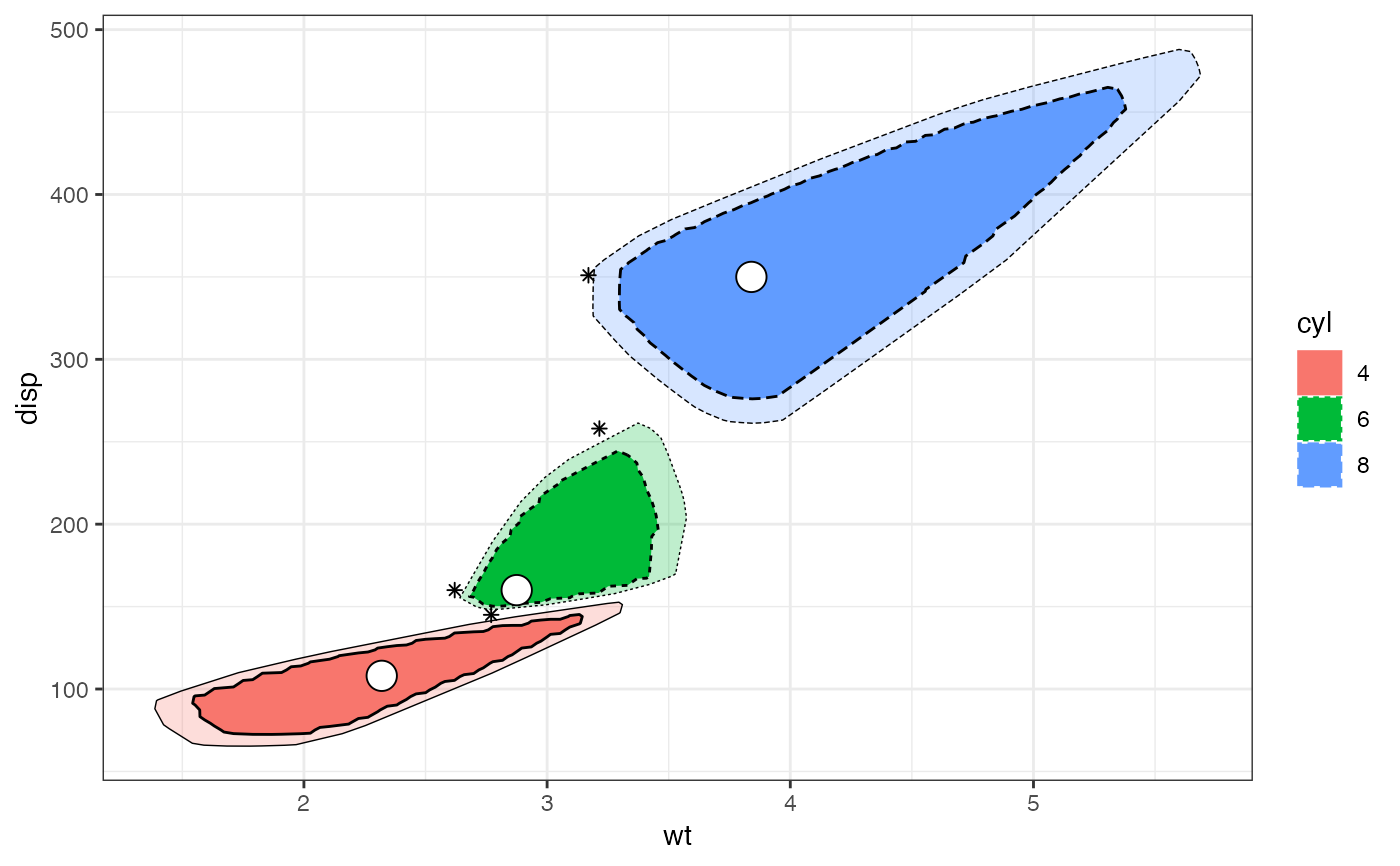
 # using normally unmapped aesthetics
p + geom_bagplot(
fraction = 0.4, coef = 1.2,
aes(fill = cyl, linetype = cyl, color = cyl),
median.color = "black",
fence.linetype = sync(), fence.colour = "black",
outlier.shape = "asterisk", outlier.colour = "black"
)
# using normally unmapped aesthetics
p + geom_bagplot(
fraction = 0.4, coef = 1.2,
aes(fill = cyl, linetype = cyl, color = cyl),
median.color = "black",
fence.linetype = sync(), fence.colour = "black",
outlier.shape = "asterisk", outlier.colour = "black"
)