Compute geometric centers and spreads for ordination factors
stat-biplot-center.RdCompute geometric centers and spreads for ordination factors
stat_center( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "point", position = "identity", show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE, ..., fun.data = NULL, fun.center = NULL, fun.min = NULL, fun.max = NULL, fun.args = list() ) stat_rows_center( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "point", position = "identity", show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE, ..., fun.data = NULL, fun.center = NULL, fun.min = NULL, fun.max = NULL, fun.args = list() ) stat_cols_center( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "point", position = "identity", show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE, ..., fun.data = NULL, fun.center = NULL, fun.min = NULL, fun.max = NULL, fun.args = list() ) stat_star( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "segment", position = "identity", show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE, ..., fun.data = NULL, fun.center = NULL, fun.args = list() ) stat_rows_star( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "segment", position = "identity", show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE, ..., fun.data = NULL, fun.center = NULL, fun.args = list() ) stat_cols_star( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "segment", position = "identity", show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE, ..., fun.data = NULL, fun.center = NULL, fun.args = list() )
Arguments
| mapping | Set of aesthetic mappings created by |
|---|---|
| data | The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options: If A A |
| geom | The geometric object to use display the data |
| position | Position adjustment, either as a string, or the result of a call to a position adjustment function. |
| show.legend | logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
|
| inherit.aes | If |
| ... | Additional arguments passed to |
| fun.data, fun.center, fun.min, fun.max, fun.args | Functions and arguments
treated as in |
Format
An object of class StatCenter (inherits from Stat, ggproto, gg) of length 3.
An object of class StatRowsCenter (inherits from StatCenter, Stat, ggproto, gg) of length 2.
An object of class StatColsCenter (inherits from StatCenter, Stat, ggproto, gg) of length 2.
An object of class StatStar (inherits from StatCenter, Stat, ggproto, gg) of length 2.
An object of class StatRowsStar (inherits from StatStar, StatCenter, Stat, ggproto, gg) of length 2.
An object of class StatColsStar (inherits from StatStar, StatCenter, Stat, ggproto, gg) of length 2.
Biplot layers
ggbiplot() uses ggplot2::fortify() internally to produce a single data
frame with a .matrix column distinguishing the subjects ("rows") and
variables ("cols"). The stat layers stat_rows() and stat_cols() simply
filter the data frame to one of these two.
The geom layers geom_rows_*() and geom_cols_*() call the corresponding
stat in order to render plot elements for the corresponding factor matrix.
geom_dims_*() selects a default matrix based on common practice, e.g.
points for rows and arrows for columns.
Examples
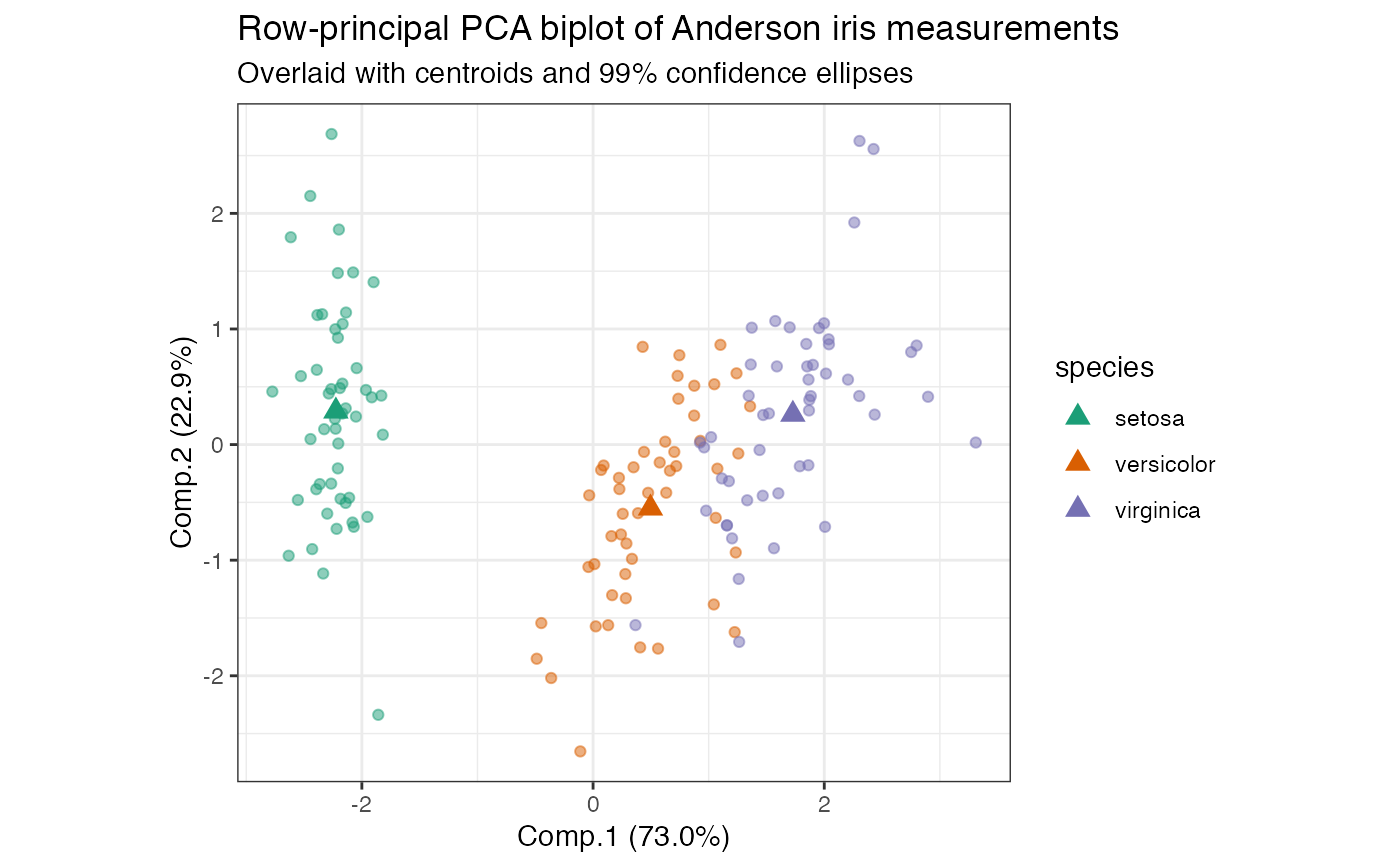
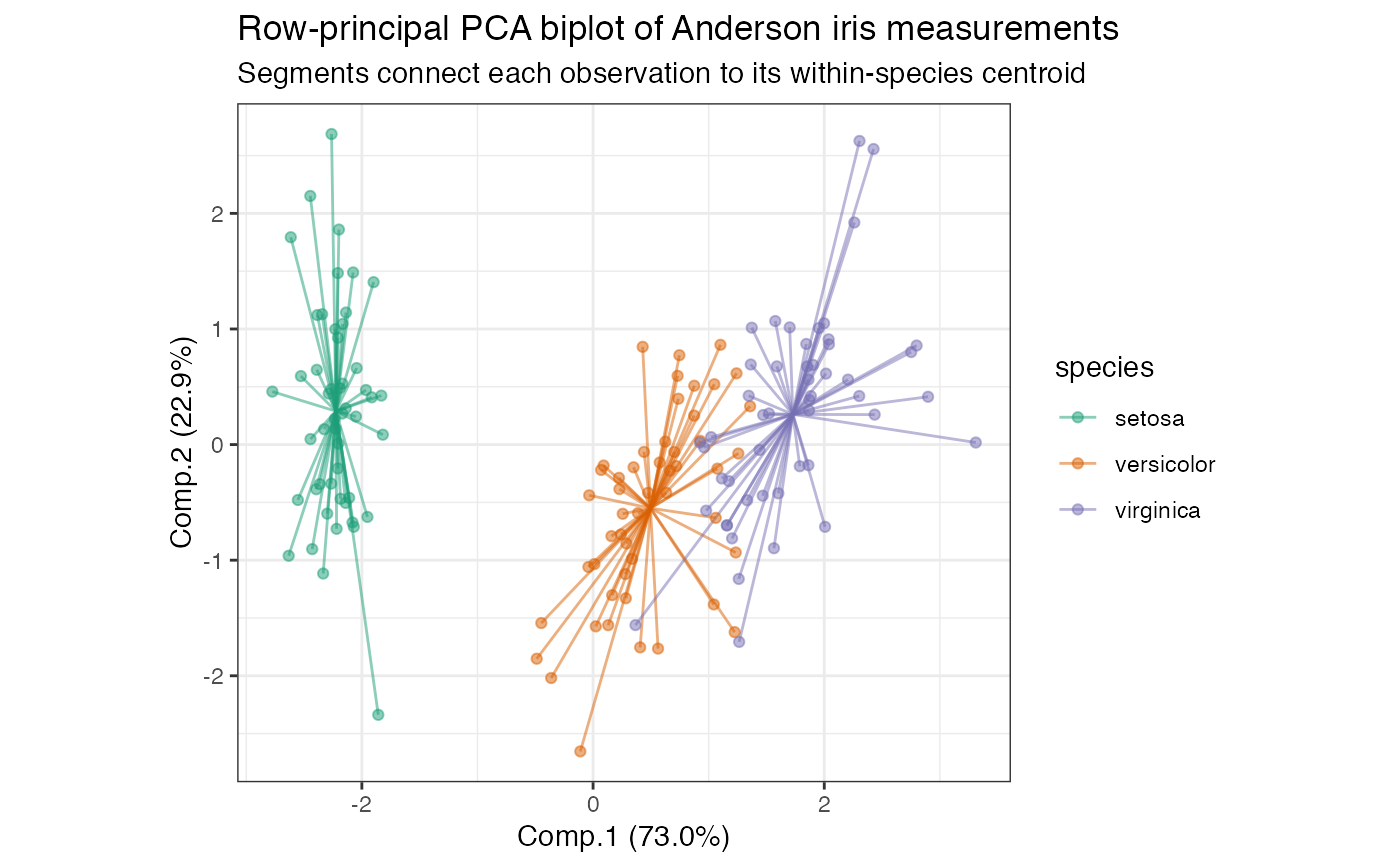
# scaled PCA of Anderson iris measurements iris[, -5] %>% princomp(cor = TRUE) %>% as_tbl_ord() %>% mutate_rows(species = iris$Species) %>% print() -> iris_pca#> # A tbl_ord of class 'princomp': (150 x 4) x (4 x 4)' #> # 4 coordinates: Comp.1, Comp.2, ..., Comp.4 #> # #> # Rows: [ 150 x 4 | 1 ] #> Comp.1 Comp.2 Comp.3 ... | species #> | <fct> #> 1 -2.26 0.480 0.128 | 1 setosa #> 2 -2.08 -0.674 0.235 ... | 2 setosa #> 3 -2.36 -0.342 -0.0442 | 3 setosa #> 4 -2.30 -0.597 -0.0913 | 4 setosa #> 5 -2.39 0.647 -0.0157 | 5 setosa #> # … with 145 more rows #> # #> # Columns: [ 4 x 4 | 0 ] #> Comp.1 Comp.2 Comp.3 ... | #> | #> 1 0.521 0.377 0.720 | #> 2 -0.269 0.923 -0.244 ... | #> 3 0.580 0.0245 -0.142 | #> 4 0.565 0.0669 -0.634 |# row-principal biplot with centroids iris_pca %>% ggbiplot(aes(color = species)) + theme_bw() + scale_color_brewer(type = "qual", palette = 2) + geom_rows_point(alpha = .5) + stat_rows_center(fun.center = "mean", size = 3, shape = "triangle") + ggtitle( "Row-principal PCA biplot of Anderson iris measurements", "Overlaid with centroids and 99% confidence ellipses" )# row-principal biplot with centroid-based stars iris_pca %>% ggbiplot(aes(color = species)) + theme_bw() + scale_color_brewer(type = "qual", palette = 2) + stat_rows_star(alpha = .5, fun.center = "mean") + geom_rows_point(alpha = .5) + ggtitle( "Row-principal PCA biplot of Anderson iris measurements", "Segments connect each observation to its within-species centroid" )